If you’ve ever worked with VMware, you know how important the VMware Server Login process is for keeping your virtualized environment running smoothly. It’s not just about logging in; it’s about safeguarding your network, managing resources, and ensuring everything stays secure. Whether you’re running a few virtual machines or managing an entire data center, getting the login process right makes a big difference.
VMware tools like vSphere Client, vCenter Server, and ESXi Hosts are the backbone of many IT infrastructures. These tools let you create, monitor, and manage virtual machines efficiently. But to access these powerful systems, you need the right login credentials and a solid understanding of how to use VMware’s different interfaces—like the vSphere Web Client or VMware Host Client.
Table of Contents
What You Will Learn
In this guide, we’ll cover:
- The core components of VMware, including vCenter Server and ESXi Hosts.
- Step-by-step instructions for logging in using different VMware clients.
- How to troubleshoot common login issues, like authentication errors and SSL warnings.
- Best practices to secure your login process, from strong passwords to multi-factor authentication.
- Tips for optimizing your VMware environment to keep it efficient and secure.
Understanding VMware Server Components
Before diving into the VMware Server Login process, it’s important to understand the key components that make up VMware’s ecosystem. These components work together to create a flexible and efficient virtualized environment. Whether you’re using a single ESXi host or managing multiple servers through vCenter Server, each piece plays a specific role in keeping things running smoothly.
vCenter Server and ESXi Hosts: The Backbone of VMware
At the core of VMware’s setup are vCenter Server and ESXi Hosts.

- vCenter Server acts as the control center for your virtualized environment. It allows you to manage multiple ESXi hosts, configure virtual machines, and monitor resources from a centralized interface. If you’re managing a larger infrastructure, vCenter Server is your go-to tool.
- ESXi Hosts, on the other hand, are the physical servers that run the hypervisor. These hosts are where your virtual machines actually live and operate. Logging directly into an ESXi host is often necessary for specific tasks like troubleshooting or managing standalone environments.
Clients: vSphere Client, Web Client, and Host Client
To access and manage these components, VMware offers several interfaces:
- vSphere Client: This is a downloadable application used to connect to vCenter Server. It’s known for its robust features and ease of use.
- vSphere Web Client: As the name suggests, this is a web-based interface for accessing your VMware environment. It’s particularly useful for those who prefer browser-based access.
- VMware Host Client: If you’re working directly with an individual ESXi host, the Host Client provides a simple and intuitive way to log in and manage virtual machines.
Table 1: VMware Clients Overview
| Client | Purpose | Access Method | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| vSphere Client | Desktop-based management of vCenter Server | Installed application | Full-featured management of large environments |
| vSphere Web Client | Web-based management of vCenter Server | Browser (via vCenter URL) | Cross-platform access and remote management |
| VMware Host Client | Browser-based management of standalone ESXi hosts | ESXi Host IP in browser | Quick configuration of individual hosts |
How These Pieces Fit Together
Think of vCenter Server as the “brains” of the operation and ESXi hosts as the “muscles.” The clients—vSphere Client, Web Client, and Host Client—are your tools for interacting with the system. Together, they provide a comprehensive solution for managing virtual environments, whether you’re dealing with a single server or an entire data center.
Accessing vCenter Server Using the vSphere Client
Logging into vCenter Server using the vSphere Client is a common way to manage your virtualized infrastructure. The vSphere Client provides a user-friendly interface packed with tools to configure, monitor, and optimize your VMware environment. Whether you’re setting up new virtual machines or tweaking existing configurations, this is where the magic happens.
Step-by-Step Guide to Logging In
Here’s a quick walkthrough to help you log into vCenter Server using the vSphere Client:
- Download the vSphere Client
If you don’t already have it, download the vSphere Client from VMware’s official website or directly from your vCenter Server’s web interface. Make sure you’re using the version compatible with your VMware setup. - Open the vSphere Client
Once installed, launch the vSphere Client application on your device. You’ll see a login screen asking for your credentials. - Enter Your Login Credentials
- Username: This is typically your domain or local username assigned for vCenter access.
- Password: Use the password associated with your account.
- Server Address: Enter the IP address or hostname of your vCenter Server.
- Handle SSL Warnings
If you encounter an SSL certificate warning, don’t panic. This happens when your vCenter Server uses a self-signed certificate. You can proceed by accepting the warning, but it’s a good idea to verify the server’s identity first. - Log In and Explore
After entering your credentials and accepting any warnings, click Login. Once inside, you’ll have access to all the tools you need to manage your virtual machines, clusters, and resources.
See my screenshot below of what the login screen should look like:
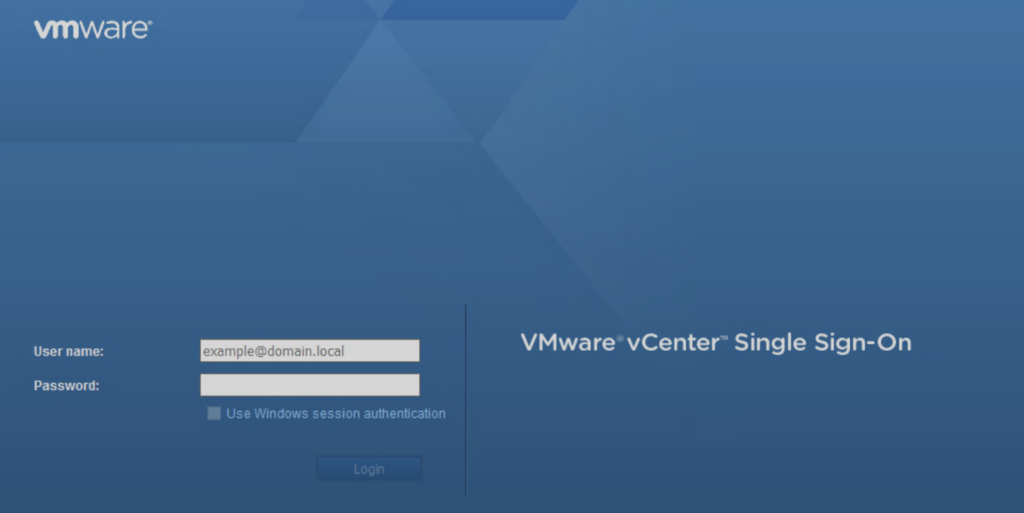
Handling SSL Certificate Warnings
SSL certificate warnings are a common hurdle during the login process. These warnings usually occur when your server uses a self-signed certificate instead of one from a trusted certificate authority. To avoid these warnings in the future, consider replacing the self-signed certificate with a trusted one. This step enhances security and eliminates browser or client pop-ups during login.
Best Practices for User Authentication
When it comes to user authentication, security should be your top priority. Here are a few tips:
- Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts accessing vCenter Server.
- Limit administrative access to essential personnel.
- Enable vCenter Single Sign-On (SSO) for centralized identity management.
- Regularly review and update user roles and permissions to ensure they align with organizational needs.
By following these steps, you can log into vCenter Server quickly and securely while minimizing potential risks.
Logging into ESXi Hosts with VMware Host Client
When managing standalone ESXi hosts, the VMware Host Client is your go-to tool. It provides a simple, browser-based interface to log in directly to an ESXi host. This is especially useful for tasks like troubleshooting, configuring virtual machines, or accessing host-specific settings.
Step-by-Step Instructions for Logging In
Follow these steps to access your ESXi host using the VMware Host Client:
- Launch a Web Browser
Open your preferred web browser and enter the IP address or hostname of your ESXi host. The format should look something like this:https://[ESXi-Host-IP-Address]. - Handle SSL Certificate Warnings
Similar to the vSphere Client, you may encounter an SSL warning when connecting to the host. This happens because ESXi uses a self-signed certificate. You can safely proceed after verifying the server’s identity. - Enter Your Credentials
- Username: Use the account associated with the host. The default username for ESXi hosts is often
root. - Password: Enter the password for the root or other assigned user account.
- Username: Use the account associated with the host. The default username for ESXi hosts is often
- Access the Host Interface
Once logged in, you’ll land on the Host Client dashboard. Here, you can view system information, manage virtual machines, and perform other administrative tasks.
Below is a screenshot of the VMWare ESXi Login screen…
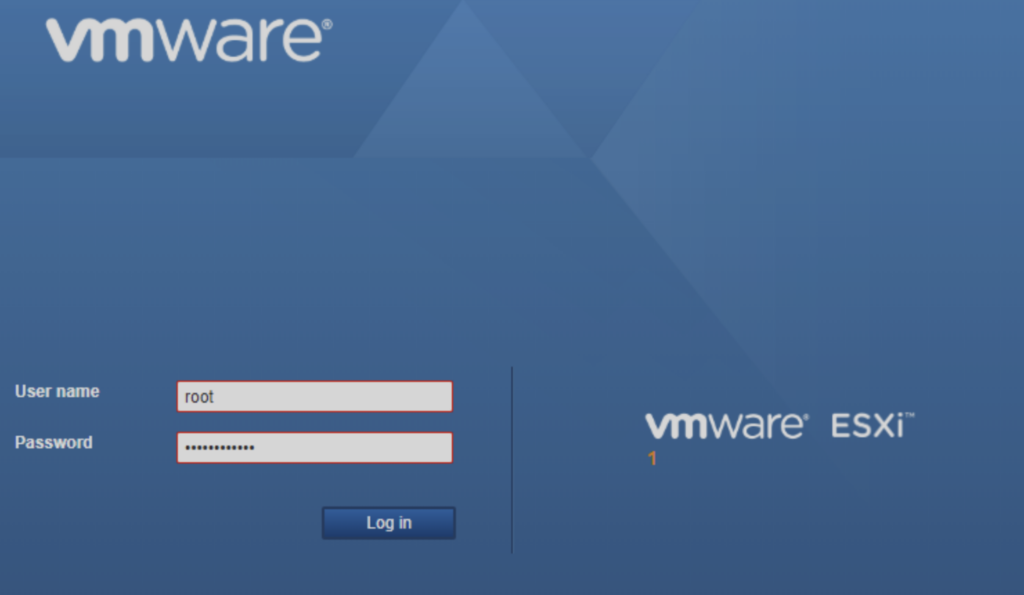
Managing Virtual Machines Post-Login
After successfully logging in, you’ll have access to tools for managing your virtual machines directly on the host. Some key features include:
- Creating New Virtual Machines: Use the wizard to set up VMs with customized configurations.
- Monitoring Performance: Check resource usage like CPU, memory, and storage.
- Power Operations: Start, stop, or restart virtual machines as needed.
- Configuring Host Settings: Update settings like networking, storage, and security options directly from the Host Client.
Why Use the VMware Host Client?
The VMware Host Client is designed for managing individual ESXi hosts without the need for a centralized management system like vCenter Server. It’s lightweight, easy to use, and works directly in your browser—no additional installation required. This makes it ideal for quick changes or standalone environments.
Tips for Secure Login Practices
When working with ESXi hosts, keep these security tips in mind:
- Change the default
rootpassword to a strong, unique one immediately after deployment. - Limit access to the ESXi host by enabling firewalls and restricting IP ranges.
- Regularly update your ESXi host to patch any vulnerabilities.
By following these steps, you’ll get the most out of the VMware Host Client while keeping your environment secure.
Utilizing the vSphere Web Client for Server Access
The vSphere Web Client offers a convenient, browser-based way to manage your VMware environment. Unlike the desktop-based vSphere Client, the Web Client doesn’t require installation, making it a flexible option for accessing vCenter Server from virtually any device.
Steps to Log In Using the vSphere Web Client
Logging into the vSphere Web Client is simple and user-friendly. Follow these steps:
- Open Your Web Browser
Launch your preferred web browser and type in the URL for your vSphere Web Client. This is typically:https://[vCenter-Server-IP-Address]/vsphere-client. - Authenticate Your Credentials
- Username: Enter your username assigned for vCenter Server access.
- Password: Use your corresponding password.
- Domain (if applicable): Specify the domain if required for authentication.
- Login Confirmation
Once your credentials are verified, you’ll be directed to the vSphere Web Client dashboard. From here, you can manage virtual machines, monitor resource usage, and configure settings.
What Makes the Web Client Different?
While the desktop-based vSphere Client and Host Client offer robust management options, the Web Client is designed with accessibility and simplicity in mind. Here’s how it stands out:
- Accessibility: No need to install software; just use a web browser.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Access it from Windows, macOS, or even Linux-based systems.
- Updated Features: VMware frequently updates the Web Client to align with modern needs and streamline workflows.
Features Available After Login
Once logged in, the vSphere Web Client opens up a wide array of tools for managing your virtual infrastructure:
- VM Management: Create, modify, and power virtual machines with ease.
- Resource Monitoring: Keep tabs on CPU, memory, and storage usage across your environment.
- User Role Management: Assign or update user roles and permissions for better access control.
- Backup and Restore: Manage snapshots and backups of your virtual machines directly through the Web Client.
Addressing Browser Compatibility Issues
Occasionally, you might run into browser compatibility problems when using the Web Client. To avoid this:
- Use a supported browser like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, or Microsoft Edge.
- Ensure that pop-ups and cookies are enabled for the vSphere Web Client URL.
- Update your browser and plugins regularly to avoid security or performance issues.
Secure Login Practices
Just like other VMware login methods, security is critical when using the Web Client. To keep your system safe:
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for an extra layer of security.
- Regularly review user access and permissions to ensure only authorized personnel have login rights.
- Use a strong, unique password for each account accessing the Web Client.
By using the vSphere Web Client, you’ll gain flexible, browser-based access to your VMware environment while maintaining robust security and efficiency.
Accessing the vCenter Server Appliance Management Interface
The vCenter Server Appliance (vCSA) Management Interface is a powerful tool for managing and configuring your vCenter Server Appliance. Whether you’re performing routine maintenance or troubleshooting an issue, this interface gives you direct access to critical system settings, logs, and resource monitoring.
How to Log into the vCenter Server Appliance Management Interface
Follow these simple steps to access the vCSA Management Interface:
- Open a Web Browser
In your browser, enter the URL for the appliance management interface. The format is:https://[vCenter-Appliance-IP-Address]:5480. - Authenticate Your Credentials
- Username: Use
rootas the default username (unless it’s been changed). - Password: Enter the root password set during the vCenter Server Appliance setup.
- Username: Use
- Access the Dashboard
Once you log in, you’ll see the appliance management dashboard, which provides an overview of system health, services, and performance.
Table 2: Essential Ports for VMware Access
| VMware Component | Port | Description |
|---|---|---|
| vCenter Server | 443 | HTTPS connection for vSphere Client and Web Client access |
| ESXi Host | 22 | SSH access for advanced troubleshooting (if enabled) |
| vCenter Server Appliance (vCSA) | 5480 | Appliance Management Interface |
| VMware Host Client | 443 | Browser-based access to standalone ESXi hosts |
Features of the Management Interface
The vCSA Management Interface is more than just a login portal—it’s a hub for managing the appliance. Here’s what you can do once you’re logged in:
- Monitor Health and Performance: Check CPU, memory, and disk usage to ensure your appliance is running efficiently.
- Manage Services: Start, stop, or restart services associated with vCenter Server.
- Update and Patch the Appliance: Apply updates and patches directly through the interface to keep your system secure and up to date.
- Access System Logs: View and download logs for troubleshooting purposes.
- Configure Network Settings: Update DNS, IP address, or other network configurations as needed.
Best Practices for Managing the vCSA Interface
To get the most out of the vCSA Management Interface, follow these tips:
- Regularly Monitor System Health: Periodic checks can help you spot issues before they escalate.
- Apply Updates Promptly: Keeping your appliance updated ensures you have the latest features and security patches.
- Secure the Root Account: Change the root password periodically and use a strong, unique password.
- Enable Alerts: Set up notifications to stay informed about system status or critical issues.
Troubleshooting Login Issues
If you encounter problems logging into the vCSA Management Interface, here are a few common fixes:
- Forgotten Password: Use the Direct Console User Interface (DCUI) on the appliance to reset the root password if needed.
- Network Connectivity Issues: Verify that the appliance’s IP address is accessible and that no firewall rules are blocking access.
- SSL Certificate Warnings: These warnings are typical with self-signed certificates. To eliminate them, replace the default certificate with one from a trusted authority.
By leveraging the vCenter Server Appliance Management Interface, you’ll have direct control over your vCenter Server settings, ensuring your environment stays secure, stable, and optimized.
Troubleshooting Common Login Issues
Logging into VMware components like vCenter Server, ESXi Hosts, or the vSphere Web Client is usually straightforward, but sometimes things don’t go as planned. Whether it’s a forgotten password, an authentication error, or a browser issue, knowing how to troubleshoot these problems can save you a lot of time and frustration.
Common VMware Login Issues and Solutions
Here’s a look at the most frequent issues users encounter and how to resolve them:
1. Authentication Errors
- The Issue: You’re entering your credentials, but access is denied.
- Possible Causes:
- Incorrect username or password.
- Account locked due to multiple failed attempts.
- Expired password.
- Solutions:
- Double-check your credentials, including case sensitivity.
- Reset your password if needed (for vCenter, use the vSphere Client or the DCUI for ESXi).
- Verify that your account hasn’t been disabled or locked in the user settings.
2. SSL Certificate Warnings
- The Issue: You see a warning about an untrusted SSL certificate when trying to log in.
- Possible Causes: VMware servers often use self-signed certificates by default.
- Solutions:
- Verify the certificate’s authenticity before proceeding.
- Install a trusted SSL certificate from a certificate authority (CA) to eliminate warnings.
3. Incorrect or Expired Login Session
- The Issue: After logging in, you’re redirected to the login page, or your session times out unexpectedly.
- Possible Causes:
- Session expiration due to inactivity.
- Browser cookies or cache issues.
- Solutions:
- Clear your browser’s cache and cookies.
- Log out from other active sessions.
- Check the session timeout settings in the VMware configuration.
4. Browser Compatibility Issues
- The Issue: You can’t access the vSphere Web Client or features aren’t loading properly.
- Possible Causes:
- Incompatible or outdated web browser.
- Solutions:
- Use a supported browser like Chrome, Firefox, or Edge.
- Update your browser to the latest version.
- Ensure that JavaScript and cookies are enabled.
5. Firewall or Network Restrictions
- The Issue: You can’t connect to your VMware server at all.
- Possible Causes:
- Network firewalls or rules blocking access.
- Solutions:
- Verify that the necessary ports (e.g., 443 for HTTPS) are open.
- Test network connectivity using tools like
pingortracert.
Advanced Troubleshooting Tips
If the basic fixes don’t resolve your login issues, here are some additional steps to try:
- Check System Logs: Logs in vCenter Server or ESXi can provide detailed error messages that point to the root cause.
- Restart VMware Services: If services like
vpxd(vCenter Server service) are unresponsive, restarting them may help. - Reboot the Appliance or Host: As a last resort, a reboot can sometimes clear stuck processes or memory-related issues.
Preventing Login Issues in the Future
To avoid common login issues down the road, follow these best practices:
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adding an extra layer of security reduces unauthorized access.
- Keep Passwords Updated: Set reminders for users to update their passwords regularly.
- Monitor System Health: Use VMware’s health monitoring tools to proactively identify potential problems.
- Document Changes: Maintain a log of password updates, role changes, and system updates for quick reference.
By addressing these common issues and implementing preventive measures, you’ll ensure a smoother experience with VMware Server Login.
Best Practices for Secure VMware Server Login
Ensuring the security of your VMware Server Login is critical to protecting your virtualized environment. With cyber threats on the rise, a proactive approach to access management can make all the difference. By following these best practices, you’ll keep your systems secure while maintaining efficient access for authorized users.
1. Use Strong Password Policies
A weak password can be the easiest way for attackers to access your VMware environment. To minimize this risk, implement these password guidelines:
- Complexity: Require a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Length: Enforce a minimum password length of 12–16 characters.
- Regular Updates: Set policies for users to change passwords periodically (e.g., every 90 days).
- Avoid Reuse: Prevent users from reusing old passwords.
These steps ensure that login credentials remain robust and harder to compromise.
2. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Adding multi-factor authentication (MFA) to your VMware login process significantly enhances security. With MFA, users must verify their identity using something they have (like a phone) in addition to their password. Popular methods include:
- Authentication Apps: Tools like Google Authenticator or Duo Security.
- Hardware Tokens: Physical devices that generate time-sensitive codes.
MFA makes it far more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access, even if they manage to steal a password.
3. Limit Administrative Access
Not everyone needs full administrative privileges. To reduce risks:
- Assign roles and permissions based on the principle of least privilege—users should only have access to the resources they need for their job.
- Regularly review user roles and permissions to ensure they align with current responsibilities.
- Disable inactive accounts to reduce unnecessary access points.
4. Keep VMware Components Updated
Outdated software can leave your system vulnerable to security exploits. Stay ahead of potential threats by:
- Applying Patches: Regularly check for and install updates for vCenter Server, ESXi Hosts, and clients like the vSphere Web Client.
- Monitoring VMware Security Advisories: Subscribe to VMware’s security alerts to stay informed about vulnerabilities and fixes.
5. Secure Remote Access
With many users managing VMware environments remotely, securing remote connections is essential:
- Use VPNs: A secure virtual private network ensures encrypted access to your VMware servers.
- Restrict IP Ranges: Allow access only from trusted networks or specific IP addresses.
- Enable Firewalls: Use built-in firewalls in ESXi Hosts and vCenter Server to control incoming and outgoing traffic.
6. Audit and Monitor Activity
Keeping a close eye on system activity can help you spot suspicious behavior early. Here’s what to focus on:
- Enable Logging: Ensure logging is active for all VMware components, including login attempts and configuration changes.
- Use vRealize Log Insight: VMware’s log management tool can provide advanced analytics and alerts.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Review logs and audit trails periodically to identify anomalies or unauthorized activity.
Why These Practices Matter
Following these best practices doesn’t just secure your VMware environment—it also creates a more efficient and reliable system. Whether you’re managing a single ESXi Host or an extensive vCenter Server deployment, a strong focus on access management and security will help you avoid downtime, data breaches, and costly recovery efforts.
By taking the time to implement these measures, you’re investing in the long-term health and stability of your VMware infrastructure.
FAQs
How do I access vCenter Server?
You can access vCenter Server using the vSphere Client (desktop) or the vSphere Web Client (browser). Simply input the vCenter Server’s IP or hostname, your username, and password, then log in.
Why am I getting an SSL certificate warning during login?
SSL warnings often occur because VMware uses self-signed certificates by default. You can either accept the warning or replace the self-signed certificate with one from a trusted certificate authority.
What should I do if I forget my ESXi host password?
If you’ve forgotten the root password for an ESXi host, you’ll need to reboot the host and follow VMware’s recovery steps. Unfortunately, there’s no built-in password recovery tool for ESXi.
Can I log into VMware remotely?
Yes, you can access VMware servers remotely using the vSphere Web Client, VMware Host Client, or via secure VPN connections to your network. Just ensure you have the correct credentials and permissions.
What are the most important ports for VMware login?
The key ports include 443 for HTTPS connections (vSphere Client, Web Client, and Host Client) and 5480 for the vCenter Server Appliance Management Interface.
Wrapping Up
Logging into your VMware servers securely and efficiently is at the heart of managing a reliable virtualized environment. From understanding the roles of vCenter Server, ESXi Hosts, and the various client tools like the vSphere Client and vSphere Web Client, to troubleshooting login issues and adopting best practices, each step plays a role in keeping your system secure and running smoothly.
By following the guidelines shared in this guide, such as enabling multi-factor authentication, using strong password policies, and staying on top of updates, you’re not just logging in—you’re safeguarding your organization’s critical infrastructure. Whether you’re a seasoned VMware admin or just getting started, these tips will help you confidently handle your VMware Server Login process.

