It’s frustrating when your MacBook won’t connect to Wi-Fi, especially when you’ve got work to finish or shows to stream. Whether it’s a sudden issue or an ongoing problem, Wi-Fi connectivity problems can quickly disrupt your day. Thankfully, there are solutions to get your MacBook back online without too much hassle.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about fixing Wi-Fi issues on your MacBook. From basic checks to advanced troubleshooting, this step-by-step approach ensures you won’t miss a thing. Let’s get started and resolve those MacBook Wi-Fi issues for good!
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Wi-Fi Connectivity Issues on MacBook
Wi-Fi problems on a MacBook can range from annoying to downright baffling. Whether your MacBook isn’t detecting networks, keeps disconnecting, or shows that it’s connected but won’t load any pages, understanding what’s happening is the first step toward a solution.
Wi-Fi background for MacBooks
Your MacBook connects to Wi-Fi using an internal wireless card that communicates with your router via radio signals. This seamless process can be disrupted by several factors, such as interference, outdated software, or hardware glitches. While Apple designs its devices for reliability, occasional issues are inevitable.
Common Symptoms of Wi-Fi Connectivity Problems
If you’re experiencing any of these issues, you’re not alone:
- Network Not Detected: Your MacBook doesn’t show available Wi-Fi networks.
- Connection Drops Frequently: Wi-Fi keeps disconnecting without warning.
- Slow Speeds: Your MacBook is connected, but the internet feels sluggish.
- Connection, but No Internet: Wi-Fi appears connected, yet webpages won’t load.
These symptoms can stem from simple fixes like software updates or more complex causes, such as hardware failures. Identifying these problems is essential for choosing the right troubleshooting steps.

2. Preliminary Checks
Before diving into more advanced troubleshooting, it’s always a good idea to rule out the basics. Sometimes, the simplest fixes can get your MacBook back online in no time. Let’s go over the quick checks first.
2.1 Ensure Wi-Fi Is Enabled
This might sound obvious, but it happens more often than you’d think. Sometimes Wi-Fi gets turned off accidentally, especially if you’ve been tweaking settings or using airplane mode.
- Click the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar at the top of your screen.
- If it says “Wi-Fi: Off”, click it and select Turn Wi-Fi On.
- If the icon isn’t there, go to System Settings > Network and enable it.
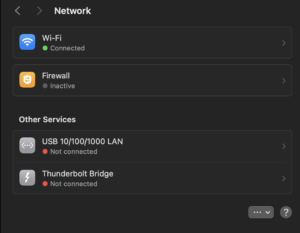
Quick Tip: If you can’t find your Wi-Fi icon, ensure it’s enabled under Control Center settings.
2.2 Check for Physical Obstructions and Interference
Your Wi-Fi signal can be impacted by what’s around your router. Walls, furniture, and even appliances like microwaves can weaken or block the signal.
Here’s how to optimize:
- Place your router in a central, open location.
- Avoid placing it near metal objects or thick walls.
- Keep it away from devices like cordless phones, baby monitors, or microwaves.
If you’re unsure whether signal strength is the issue, try moving closer to the router. If the connection improves, interference might be the culprit.
2.3 Verify Network Selection
Sometimes your MacBook might connect to the wrong Wi-Fi network, like an open network or a guest connection with limited access.
Steps to verify:
- Click the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar.
- Look for the checkmark next to your network name.
- If it’s not your primary network, select the correct one and enter the password if prompted.
Pro Tip: If you see multiple networks with similar names, ask your network admin (or check your router) to confirm the correct SSID.
Checklist: Quick Fixes for Preliminary Issues
| Issue | Quick Fix |
|---|---|
| Wi-Fi turned off | Enable it via the menu bar or settings. |
| Poor router placement | Move your router to a central location. |
| Wrong network selected | Switch to the correct Wi-Fi network. |
If these preliminary checks don’t solve the problem, don’t worry. Let’s move on to basic troubleshooting steps that are just as simple but a bit more hands-on.
3. Basic Troubleshooting Steps
If the quick checks didn’t work, don’t panic. Most MacBook Wi-Fi issues can be solved with a few straightforward troubleshooting steps. Let’s roll up our sleeves and dig in.
Restart Your Mac and Router
A simple reboot often works wonders. It clears temporary glitches and refreshes the connection.
Steps for your MacBook:
- Click the Apple menu in the top-left corner.
- Select Restart and confirm.
Steps for your router:
- Turn off the router and unplug it from the power source.
- Wait about 30 seconds, then plug it back in and turn it on.
- Wait for the router to reboot completely (look for stable indicator lights).
Why it works: Restarting your devices clears cache and re-establishes the network connection.
Forget and Reconnect to the Wi-Fi Network
If restarting didn’t do the trick, try forgetting the Wi-Fi network and reconnecting. This can fix issues caused by corrupted connection data.
Steps:
- Click the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar and select Wi-Fi Settings.
- Find your network under Known Networks and click the … or Remove button.
- Reconnect by selecting your network and entering the password.
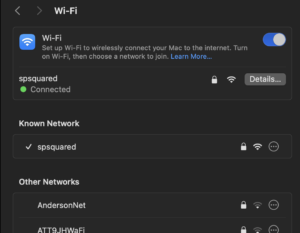
Pro Tip: Double-check the password—you’d be surprised how often typos are the culprit.
Update macOS
Running an outdated macOS can sometimes cause Wi-Fi glitches, especially if the update includes bug fixes for network issues.
Here’s how to check for updates:
- Open System Settings and select General > Software Update.
- If an update is available, click Update Now.
- Restart your Mac once the update is installed.
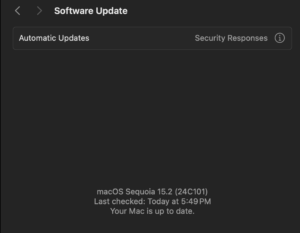
Good to know: Updating your macOS also refreshes drivers, which can solve compatibility issues with your router.
Quick Fix Summary
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Temporary glitches | Restart your Mac and router. |
| Corrupted network data | Forget and reconnect to the network. |
| Outdated software | Install the latest macOS update. |
If your MacBook is still not connecting to Wi-Fi, don’t worry. There are more advanced steps you can take, and we’ll tackle those next.
4. Advanced Troubleshooting
If basic troubleshooting didn’t resolve your MacBook Wi-Fi issues, it’s time to dive into more advanced techniques. Don’t worry—these steps are still manageable, and I’ll guide you through them.
Renew DHCP Lease
Renewing your DHCP lease can fix connectivity issues by refreshing the IP address your MacBook gets from the router.
Here’s how:
- Go to System Settings > Network.
- Select your Wi-Fi network and click Details.
- Click on TCP/IP
- Find the Renew Lease button and click it.
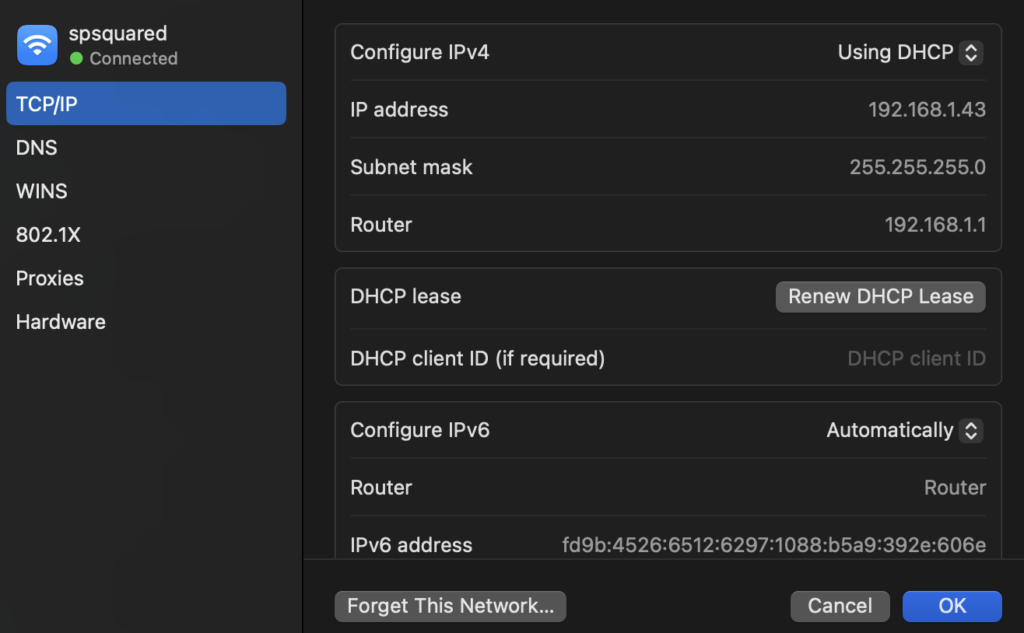
Why it helps: A renewed DHCP lease clears out conflicts with your network’s IP address.
Modify DNS Settings
Sometimes, your MacBook struggles to connect because of DNS server issues. Switching to a public DNS server, like Google DNS, can improve connection reliability.
Steps to change DNS:
- Open System Settings > Network.
- Select your Wi-Fi network and click Details.
- Go to the DNS tab.
- Replace the current DNS with these:
- 8.8.8.8
- 8.8.4.4
- Click Save and reconnect to your network.
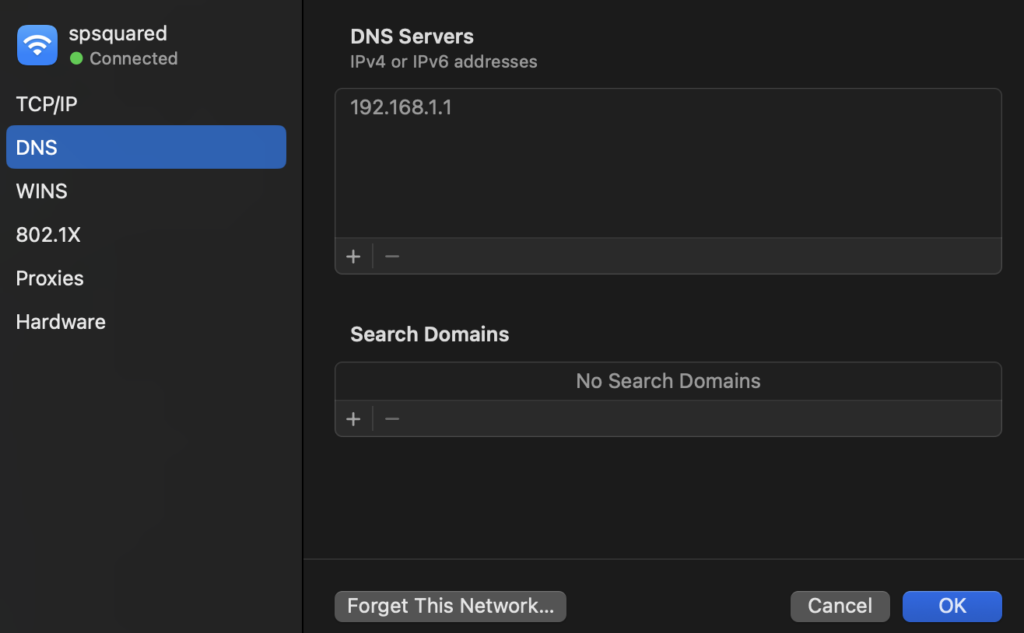
Good to know: Using public DNS servers can also speed up your internet.
Reset Network Configuration
If the issue persists, resetting your network settings might do the trick. This will clear all network data and let you start fresh.
Here’s how to reset:
- Go to System Settings > General > Transfer or Reset.
- Select Erase all Content and Settings and choose Network Settings.
- Follow the prompts to complete the reset.
Keep in mind: You’ll need to reconnect to your Wi-Fi network afterward, so have your password handy.
Check for VPN or Security Software Interference
VPNs and security software can occasionally interfere with your MacBook’s Wi-Fi connection. Temporarily disable these to see if they’re causing the problem.
- For VPNs: Disconnect using the app or your network settings.
- For antivirus or firewalls: Pause the protection temporarily.
If disabling these resolves the issue, update the software or adjust its settings for compatibility.
Advanced Troubleshooting Recap
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| IP address conflicts | Renew DHCP lease. |
| DNS issues | Switch to Google’s public DNS servers. |
| Corrupted network settings | Reset network configuration. |
| Software interference | Disable VPN or security tools. |
Still no luck? Don’t worry—there’s more help ahead. Let’s explore the diagnostic tools built into macOS.
6. Hardware Considerations
If software fixes haven’t resolved your MacBook’s Wi-Fi issues, it might be time to consider potential hardware problems. While MacBooks are known for their reliability, wear and tear or specific hardware glitches can sometimes impact connectivity.
6.1 Check for Hardware Issues
Before jumping to conclusions, check if the issue might be hardware-related:
- Does Wi-Fi work on other devices? If your router works fine for other devices, the issue might be specific to your MacBook.
- Does the problem occur everywhere? If Wi-Fi fails no matter which network you connect to, your MacBook’s Wi-Fi card might need attention.
Signs of hardware problems:
- Wi-Fi networks don’t appear at all.
- The connection constantly drops, even after resets.
- The MacBook overheats or shows physical damage near the antenna.
6.2 Reset SMC and NVRAM/PRAM
Resetting the System Management Controller (SMC) and NVRAM/PRAM can fix hardware-related quirks, including Wi-Fi connectivity issues.
How to Reset the SMC:
- Shut down your MacBook.
- On a Mac with an Intel chip:
- Press and hold Shift + Control + Option + Power for 10 seconds.
- Release all keys and turn the MacBook back on.
- For M1/M2 Macs, just restart your MacBook—SMC resets automatically.
How to Reset NVRAM/PRAM:
- Shut down your MacBook.
- Turn it back on and immediately hold Option + Command + P + R.
- Keep holding for about 20 seconds, then release.
Why this helps: These resets clear stored configurations that might be interfering with Wi-Fi.
When Hardware Repair Might Be Necessary
If resetting doesn’t help, or if your MacBook continues to fail across multiple networks, it could indicate a faulty Wi-Fi card or antenna. In this case:
- Visit an Apple Store or an Authorized Service Provider for diagnostics.
- If your MacBook is under warranty, repairs might be free.
If none of these steps solve your Wi-Fi issues, it might be time to bring in the pros. Let’s cover when and how to seek professional help in the next section.
7. Still not fixed? Get additional Support
If you’ve tried everything and your MacBook still refuses to connect to Wi-Fi, it might be time to bring in the experts. While most connectivity issues can be fixed with the steps we’ve covered, there are situations where professional help is the best option.
Where to Get Help
When seeking assistance, stick with trusted sources:
- Apple Support: Start by contacting Apple Support online or via their app. They might guide you through additional troubleshooting steps or arrange a repair.
- Apple Store or Authorized Service Provider: Schedule a visit to an Apple Store or certified technician. They have the tools to diagnose and repair your MacBook.
- Local Repair Shops: If you’re out of warranty, a trusted local repair shop might offer a more budget-friendly solution.
How to Prepare for Your Visit
To make the process smoother:
- Back Up Your Data: Use Time Machine or iCloud to back up your files before handing over your MacBook.
- Document the Issue: Take note of what’s been happening, including when the problem started and what steps you’ve already tried.
- Bring Essential Info: If you’re visiting Apple, bring proof of purchase and any accessories, like chargers.
Final Thoughts
Dealing with a MacBook that won’t connect to Wi-Fi can be a real headache, but the good news is that most issues are fixable with a bit of patience and troubleshooting. From quick checks like ensuring your Wi-Fi is enabled to advanced fixes like resetting the SMC or updating your DNS settings, this guide covers everything you need to get back online.
Before you panic, remember:
- Start simple: Basic checks like restarting your Mac or router often work.
- Explore advanced fixes: Adjusting network settings or using macOS diagnostics can tackle trickier issues.
- Know when to ask for help: If nothing works, professional support is always an option.
Wi-Fi problems may feel overwhelming, but you’ve now got a toolbox of solutions to tackle them. So the next time your MacBook acts up, you’ll know exactly what to do. And hey, if all else fails, a quick trip to the Apple Store might be the fastest way to solve the problem.
Good luck, and happy browsing! If this guide helped you, share it with someone else who might be facing the same issue. Let’s keep everyone connected! 😊
FAQs
Why won’t my MacBook connect to WiFi even though the password is correct?
This could be due to incorrect network settings, a temporary glitch, or the network itself may be experiencing issues.
How do I reset my MacBook’s WiFi settings?
You can reset your network settings by removing the WiFi service in Network Preferences and then adding it back.
Can a VPN cause my MacBook to lose WiFi connection?
Yes, VPNs can sometimes interfere with your internet connection due to configuration errors or outdated software.
What should I do if my MacBook connects to WiFi but can’t access the internet?
Check for DNS issues, ensure you don’t have a static IP set up, and try renewing the DHCP lease. Also, verify if the problem persists on other devices to rule out router issues.

