Experiencing WiFi disconnections on a MacBook can be a significant hindrance, affecting everything from daily productivity to leisure activities. Stable internet connectivity is not just a convenience but a necessity for MacBook users in today’s digital age.
This article dives into the common causes behind MacBook WiFi keeps disconnecting, offering a comprehensive guide to troubleshooting steps and expert advice to ensure a seamless online experience.
Table of Contents
Common Causes of WiFi Disconnecting on MacBook
Hardware Limitations and Interferences
Several hardware-related factors can contribute to WiFi disconnections on a MacBook. These include:
- Outdated WiFi Modules: Older MacBook models may have WiFi modules that struggle to maintain connections with modern routers, especially those using newer WiFi standards like WiFi 6.
- Physical Obstructions: Thick walls, metal objects, and other physical barriers between your MacBook and the WiFi router can weaken the signal, leading to disconnections.
- Interference from Other Devices: Microwaves, cordless phones, and other electronic devices operating on the same frequency as your WiFi can cause interference, disrupting your MacBook’s WiFi connection.
Comparison of Common Causes and Solutions for WiFi Disconnections
| Cause | Solution | Preventive Measure |
|---|---|---|
| Outdated software | Update macOS | Regularly check for updates |
| Interference | Change WiFi bands | Optimize router placement |
| Incorrect settings | Adjust network preferences | Regularly review network settings |
Software Glitches and Updates
Software issues can also lead to WiFi connectivity problems:
- Operating System Bugs: Occasionally, macOS updates may introduce bugs that affect WiFi performance. Conversely, outdated macOS versions may lack the latest fixes and improvements for stable connectivity.
- Driver Incompatibility: WiFi driver issues can arise, especially after a macOS upgrade, if the drivers are not fully compatible with the new version.
Network Settings and Configuration Issues
Improper network settings can be a root cause of WiFi disconnections:
- Incorrect Configuration: Misconfigured network settings on your MacBook or router can lead to unstable connections.
- DHCP Issues: If your MacBook fails to obtain an IP address automatically from the router, it may frequently disconnect from the WiFi.
- Overloaded Networks: Connecting to a crowded WiFi channel can result in disconnections. Switching to a less congested channel on your router may improve stability.
Understanding these common causes is the first step towards diagnosing and resolving WiFi disconnection issues on your MacBook.
Troubleshooting Steps to Fix WiFi Disconnections
Restarting Your MacBook and Router
A fundamental yet often effective solution is to restart both your MacBook and WiFi router. This simple action can clear temporary glitches affecting the WiFi connection. To restart your MacBook, click on the Apple menu and select “Restart.” For the router, unplug it from the power source, wait for about 30 seconds, and plug it back in. This process can refresh your network connection, resolving transient issues.
Updating Your macOS
Ensuring your macOS is up to date is crucial for maintaining WiFi stability. Apple frequently releases updates that improve system performance and fix known bugs, including those related to WiFi connectivity. To check for updates:
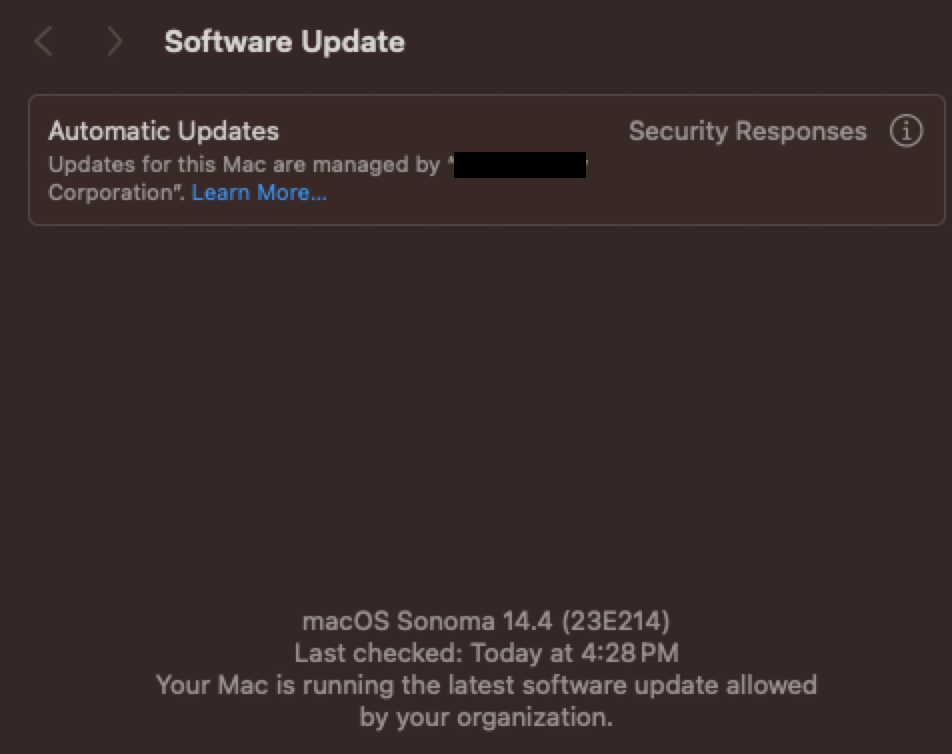
- Open “System Settings.”
- Click on “General” and then “Software Update.”
- If an update is available, click “Update Now” to install.
Forget and Reconnect to the WiFi Network
Forgetting the WiFi network and reconnecting can resolve connection issues related to incorrect settings or corrupted profiles. To do this:
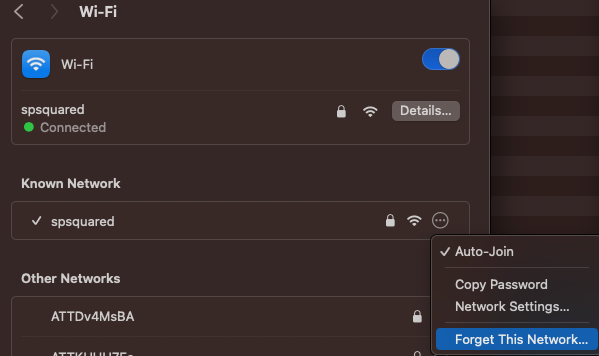
- Go to “System Settings” > “Network.”
- Select “WiFi” and click on “Advanced.”
- Under the Known Network section, click the 3 dots (…) button, and then “Forget this Network.”
- Reconnect by selecting your WiFi network from the list and entering the password.
Renewing DHCP Lease and Using Custom DNS
Renewing the DHCP lease can help resolve IP address conflicts, while using a custom DNS server can improve internet speed and reliability. To renew the DHCP lease:
- Navigate to “System Settings” > “Network.”
- Select “WiFi” and click “Advanced.”
- Go to the “TCP/IP” tab and click “Renew DHCP Lease.”
To set a custom DNS: - In the “Advanced” settings, switch to the “DNS” tab.
- Click the plus (+) button to add a new DNS server (e.g., 1.1.1.1 for Cloudflare or 8.8.8.8 for Google).
The location of the above section has changed in recent MacOS version. In the System Settings menu, you can search for “TCP” and then click on “TCP/IP”. See image below:
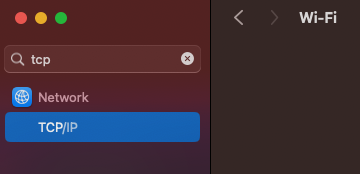
Advanced Solutions for Persistent WiFi Issues
Creating a New Network Location
Creating a new network location can help reset your network settings to default, potentially resolving persistent connectivity issues. To create a new location:
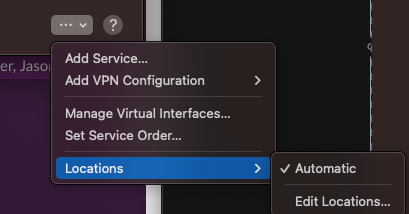
- Go to “System Settings” > “Network.”
- At the bottom of the window, find the 3 dots (…) and click and choose “Locations > Edit Locations”.
- Click the plus (+) button, name the new location, and select “Done.”
Resetting the SMC and PRAM/NVRAM
Resetting the System Management Controller (SMC) and Parameter RAM (PRAM) or Non-Volatile RAM (NVRAM) can resolve deeper hardware-related issues. The process varies depending on your MacBook model, so refer to Apple’s official support documents for instructions specific to your device.
Checking for Interference and Changing WiFi Bands
Interference from other devices can significantly impact WiFi performance. Identify potential sources of interference, such as cordless phones or microwaves, and move them away from your MacBook and router. Additionally, switching from a crowded 2.4GHz band to a less congested 5GHz band can improve WiFi stability. This setting can be adjusted in your router’s configuration interface.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Future Disconnections
Regular Software Updates
Keeping your macOS and all drivers up to date is crucial for ensuring the stability of your WiFi connection. Apple frequently releases updates that not only enhance security but also improve functionality and fix bugs that may affect connectivity.
Optimizing Network Settings
Adjusting your network settings can significantly impact the reliability of your WiFi connection. This includes selecting the optimal channel and frequency band (2.4GHz vs. 5GHz) on your router to minimize interference and congestion.
Physical Placement and Router Health
The physical placement of both your MacBook and WiFi router plays a vital role in connection quality. Ensure your router is positioned centrally to where you use your MacBook most often, away from obstructions and interference sources. Regularly rebooting your router can also maintain its health and performance.
FAQs on MacBook WiFi Connectivity
Why does my MacBook keep disconnecting from WiFi after updating macOS?
This could be due to compatibility issues between the new macOS and your WiFi hardware or settings. Checking for additional updates or resetting network settings may resolve this.
How can I prevent my MacBook from automatically disconnecting from WiFi?
Ensure your energy saver settings are not set to disconnect from WiFi to save power. Updating your software and maintaining optimal network settings can also help.
What should I do if none of the troubleshooting steps work?
Consider consulting with a professional or visiting an Apple Store for a diagnostic. There might be underlying hardware issues with your MacBook or router.
Can a VPN cause WiFi disconnection issues on MacBook?
Yes, VPNs can sometimes interfere with your network connection. Try disabling your VPN temporarily to see if that resolves the issue.
Is it possible that my MacBook’s WiFi disconnection is due to my router’s settings?
Absolutely. Router settings such as MAC filtering, firmware issues, or incompatible security protocols can cause disconnections. Reviewing and adjusting these settings may help.
Conclusion
Identifying the root cause of WiFi disconnections on your MacBook is essential for a stable online experience. By following the troubleshooting steps and preventive measures outlined, you can minimize disruptions and maintain a reliable connection. Regular updates, optimal network settings, and strategic device placement are key strategies for uninterrupted WiFi connectivity.

